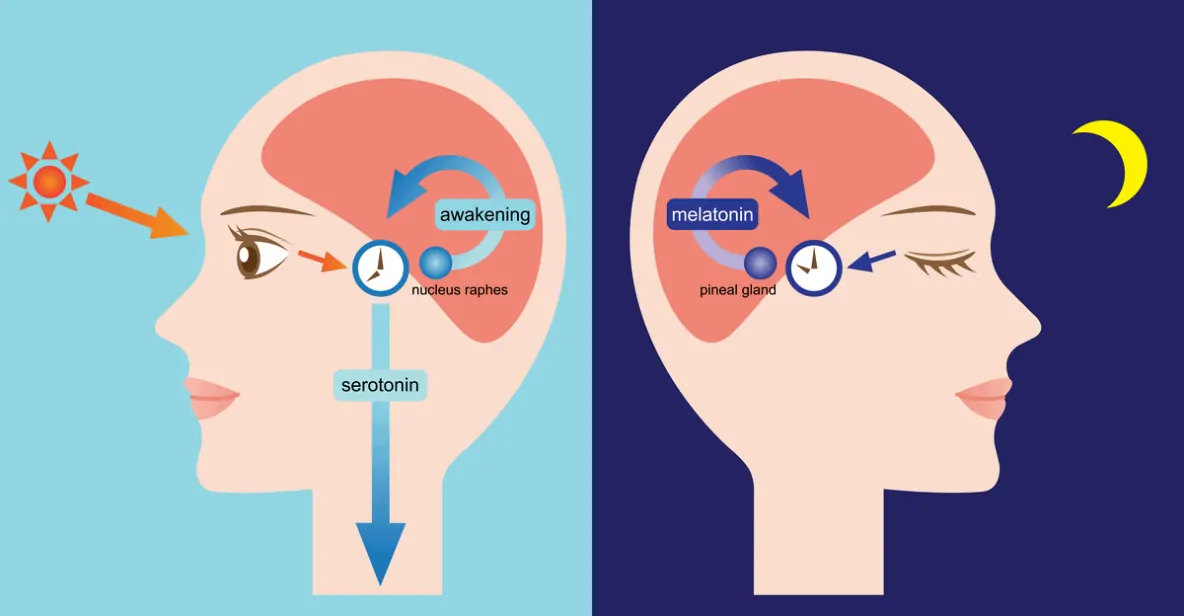
Melatonin is released by the brain according to the body’s natural circadian rhythm (our internal biological clock) to regulate the body’s natural sleep and wake cycles.
Melatonin is also used as a sleep aid to acclimate to different time zones after long-distance flights. Furthermore, some people take melatonin in the hope that it will aid muscle growth and promote fat loss by releasing more growth hormone in the body.
7 Potential Benefits of Melatonin
- Reduces Stress
- Promotes Fat Loss
- Aids Muscle Growth
- Helps Improve Sleep
- Supports Muscle Recovery
- Releases Growth Hormone
- Increases Antioxidant Activity
A significant factor of good quality, restful sleep, involves two known chemicals: growth hormone and melatonin. Growth hormone is released in short bursts when a person exercises and sleeps.
Growth hormone has a short half-life, which means that it doesn’t last long in the body; however, growth hormone’s fat-burning and muscle-building effects last long after its half-life has expired.
Research published in Cells indicates that taking melatonin before exercise can aid muscle growth, fat loss, and post-workout recovery with minimal effects on wakefulness or energy levels. On its own, melatonin will not trigger muscle growth. However, melatonin is said to provide benefits if a person has trouble sleeping or has a melatonin deficiency.
Melatonin and Growth Hormone
A study performed by the University of Seville Medical School measured the effects of melatonin supplementation on oxidative stress, immunity, and fat metabolism before intense exercise.
In the study, athletes took either 6 mg of melatonin or a placebo one hour before continuous intense exercise. At the end of the study, researchers discovered that melatonin increased antioxidant activity by a significant amount and lowered exercise-induced oxidative stress.
The researchers also noticed that the melatonin group increased their fat metabolism during workouts while experiencing improved immunity.
Additional research by scientists at Baylor University reported that male athletes who took 5 milligrams of melatonin an hour before a leg workout had higher levels of growth hormone before and after training compared to athletes who took a placebo supplement.
The study discovered that test subjects who took a small amount of melatonin (0.5 milligrams), had higher growth hormone levels after training.
Together, these studies appear to support the use of melatonin for increasing growth hormone secretion. Does this mean it’s good to take melatonin to boost growth hormone levels? In short, the answer is no. While melatonin is a natural hormone produced by the body, it’s one of the most questionable supplements, and its side effects can be severe.
Safety and Side Effects
Melatonin is only available in America as an over-the-counter dietary supplement. Furthermore, research into melatonin is incomplete and requires more investigation. Some studies show that long-term melatonin use can disrupt the body’s natural hormone levels, even sabotaging sleep.
In the words of Dr. Wurtman, the MIT neuroscientist who originally suggested melatonin as a possible sleep aid:
“With some hormones, if you take too much, you can put your body in danger. With melatonin, you’re not in danger, but you’re also not very comfortable. Melatonin won’t kill you, but it will make your life pretty miserable.”
Dr. Wurtman, MIT
Using melatonin can also induce hypothermia. Body temperatures drop during the release of melatonin, as the hormone, prolactin, is stimulated. This hormonal imbalance can cause severe issues, including kidney and liver problems in men.
Recommended Dosage
A dose of 0.2-5 mg of melatonin is considered safe. However, side effects can still occur, and you should be aware of the potential dangers of melatonin supplements.
Effectiveness of Melatonin
While there’s no evidence to suggest that too much melatonin is fatal or even close to life-threatening, exceeding the recommended dose can upset the body’s natural processes and circadian rhythm.
Overall, the potential risks associated with melatonin supplementation far outweigh the benefits. It’s much more effective and safer to get your dose of melatonin from good-quality sleep as opposed to taking melatonin supplements.